In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for businesses of all sizes. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent, companies cannot afford to take a passive approach to security. The threat landscape and attack surface of organizations has immensely increased over the past few years.
In recent years, the concept of “Zero Trust” has gained significant traction as an effective security strategy for businesses looking to protect their assets and data. But despite its benefits, many companies still delay its implementation, putting themselves at risk. We’ll explore why companies shouldn’t delay Zero Trust and the potential consequences of doing so.
The State of Cybersecurity Today
Before we dive into zero trust and its challenges, let’s have a look at the state of cybersecurity to have an idea of what are we dealing with in terms of cybersecurity threats and data breaches.
According to ESENTIRE’s official Cybercrime report the average cost of cybercrime is predicted to hit $8 trillion in 2023 and exponentially rise to $10.5 Trillion by the year 2025.
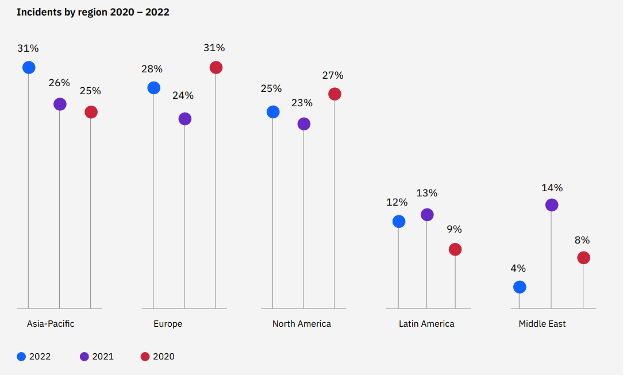
As per IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Report 2022, the most attacked region is the Asia Pacific accounting for approximately 31% of the incidents recorded by Incident Response.
Figure 1. Incident By Regions 2020-2022. Source IBM X-Force
Further investigations by IBM revealed that Data extortion was the most common attack impact on organizations with phishing being the top initial access vector of compromise identified in 41% of cybersecurity incidents.
Further statistics by Verizon data breach report states that Ransomware attacks have increased by 13% as compared to the last 5 years.
It is quite evident from the above stats that cybersecurity incidents and data breaches won’t stop and will continue to rise at the same frequency as they were previously. To battle against high volume and complex cybersecurity attacks organizations must adopt a proactive approach and utilize security architectures and models like zero trust to mitigate and contain the previously mentioned attacks.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security framework that emphasizes the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It is designed to provide a comprehensive security approach that protects assets and data by ensuring that no user, device, or application is automatically trusted, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the corporate network. Zero Trust operates under the assumption that every access request is potentially malicious and should be thoroughly verified before granting access.
In a nutshell “The Zero Trust” model is built around three core principles:
- Identify
- Verify
- Enforce
The first principle, identify, involves identifying all users, devices, and applications that require access to resources. This involves creating a comprehensive inventory of all assets, including data, applications, and services, and mapping out their relationships with each other.
The second principle, verify, involves thoroughly verifying the identity and security posture of all users, devices, and applications before granting access. This involves implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and continuously monitoring all access requests for signs of suspicious activity.
The third principle, enforce, involves enforcing strict access control policies that limit access to resources based on the user’s role, location, and device posture. This involves implementing granular access control policies and micro-segmentation to ensure that each user only has access to the resources they need to perform their job, and nothing more.
Zero Trust is not a single product or solution, but rather a comprehensive security framework that incorporates a range of security measures, such as encryption, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring. It also involves a cultural shift towards a security-centric mindset, where security is seen as a fundamental component of business operations, rather than an afterthought. Zero Trust Architectures are well-suitable and effective for environments that come under the hood of critical infrastructures due to their IT/OT integrations.
Challenges faced by organizations to adopt Zero Trust Model
For more than a decade, the idea of a Zero Trust security architecture has been around but the pace of adopting it has not seen an exponential increase over the past few years. Many organizations lack basic cybersecurity hygiene due to which sooner or later they suffer from an inevitable loss in terms of monetary and reputation.
Let’s demystify and uncover the challenges and the reasons why organizations are still hesitant and delaying adopting the zero trust model despite increasing cybersecurity attacks.
Why do companies delay Zero Trust?
Despite the clear benefits of Zero Trust, many companies delay its implementation for various reasons. One of the primary reasons is the perception that Zero Trust is too complex and time-consuming to implement. Companies may also be hesitant to implement Zero Trust due to the potential disruption to business operations and the need for significant changes to existing security policies and procedures. Additionally, some companies may feel that their existing security measures are adequate, or they may underestimate the severity of cyber threats.
Some of the pertinent challenges faced by organizations to implement zero-trust architectures are discussed below:
- Complexity: One of the primary challenges of implementing Zero Trust architecture is its complexity. Zero Trust requires an extensive and integrated system of security controls, which is time-consuming and resource intensive. The architecture must be customized to fit each organization’s unique infrastructure, which can add a layer of complexity. The complexity part is typically decreased if the organization has clearly defined trust boundaries for traffic inflows and outflows, their critical assets are identified and a holistic approach towards security is being adopted by intensive information security programs.
- Cost: Another significant challenge is the cost of implementing Zero Trust architecture. The architecture requires the integration of several security solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multifactor authentication tools, which can be expensive. On the other hand, the cost also increases if an organization has to replace legacy systems with new ones. Organizations must also allocate sufficient resources to maintain and upgrade the architecture.
- Lack of skilled personnel: Zero Trust architecture requires skilled IT personnel who are experienced in cybersecurity practices. Unfortunately, there is a shortage of cybersecurity professionals, making it challenging for organizations to find the right people to implement and maintain the architecture. Often sometimes the internal controls, processes, and policies are too vague or hard to understand and the relevant teams lose their actual objective to protect and implement the desired security controls.
- Culture: Zero Trust architecture requires a significant shift in an organization’s security culture. The architecture requires all users to adopt new security practices and mindsets, which can be challenging to achieve. Organizations must provide extensive training and awareness programs to ensure that employees are equipped with the necessary skills to implement and maintain Zero Trust.
- Perception of low risk: Many organizations perceive themselves as low-risk targets for cyber-attacks, leading to a lack of urgency in implementing Zero Trust architecture. This perception often results from a lack of understanding of the potential risks and impacts of a cyber-attack, leading to inadequate investments in cybersecurity solutions.
The risks of delaying Zero Trust
Delaying the implementation of Zero Trust can have severe consequences for companies. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent, companies that rely on traditional security measures are at greater risk of security breaches. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the network and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, resulting in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
The consequences of a security breach can be devastating for companies, both in the short and long term. In addition to financial losses, companies may face legal action, regulatory fines, and damage to their reputation, which can have long-lasting effects on their business operations.
Implementing Zero Trust can be a challenging process, but the benefits far outweigh the challenges. Zero Trust provides a comprehensive security approach that ensures the protection of assets and data, regardless of the location or user. By implementing Zero Trust, companies can reduce the risk of security breaches and improve their overall security posture. Zero Trust can also help companies meet compliance requirements and improve their ability to respond to security incidents.
Conclusion
Organizations must take cybersecurity seriously and adopt advanced security solutions such as Zero Trust architecture to protect their data and resources from cyber-attacks. While the implementation of Zero Trust architecture is complex and comes with its own set of challenges and problems, the benefits of implementing it far outweigh the costs. Organizations must carefully consider the risks and rewards of Zero Trust architecture and implement it in a way that ensures the protection of critical resources and data. By doing so, organizations can build a robust and secure cybersecurity posture that protects them from ever-evolving cyber threats.
Try Portnox Cloud for Free Today
Gain access to all of Portnox's powerful zero trust access control free capabilities for 30 days!